What is breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation is also known as augmentation mammoplasty, or a “boob job.” It’s a cosmetic surgery procedure to increase breast size and enhance breast shape, typically through breast implants or fat transfer(“fat from another part of the patient’s body”). From a cosmetic surgeon’s perspective, the primary objective of breast augmentation is to enhance a patient’s natural proportions and create a more symmetrical, aesthetically pleasing breast profile.
For some women, breast augmentation is a way to feel more confident. For others, it’s part of rebuilding the breast for various conditions. The exact procedure is tailored to meet a woman’s individual needs.

Who is a good candidate for breast augmentation?
Good candidates for breast augmentation typically include women who are in good overall health, not pregnant or breastfeeding, whose breasts are fully developed, and who have realistic expectations about the procedure. They may consider breast augmentation for various reasons, such as:
- Breasts are too small.
- You are dissatisfied with your breasts losing shape and volume after genetics, pregnancy, weight loss, or aging.
- Breasts are asymmetrical. One or both breasts failed to develop normally or have an elongated shape.
- Correct uneven breasts after breast surgery for other conditions.
How much does breast augmentation cost?
Generally, the cost of breast augmentation surgery can vary widely depending on various factors. In the USA, the average cost of breast augmentation surgery is $4,294. In the UK, breast implant surgery costs around £3,500 to £8,000. This cost is only part of the total price – it does not include anesthesia, operating room facilities, or other related expenses.
Before surgery, many plastic surgeons offer patient financing plans for breast augmentation, so be sure to ask about the items that may be included in the breast augmentation cost.
Breast augmentation costs may include:
- Pre-operative consultations
- Medical tests
- Surgeon’s fee
- Anesthesia fees
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- The implants themselves
- Medications
- Post-surgery garments and post-operative care
- Follow-up appointments
- Also, consider the time costs involved in the procedure and recovery.
Remember that the surgeon’s experience and your comfort with him or her are just as important as the final cost of the surgery. It’s important to consult with a board-certified plastic surgeon to get an accurate estimate tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. Additionally, be sure to discuss all potential costs and any financing options available.
What are the risks of breast augmentation?
As with any surgery, there are risks, before surgery, you will be asked to sign consent forms to ensure that you fully understand the breast augmentation procedure and any risks and potential complications.
Possible breast augmentation surgery risks include:
Anesthesia risks:
As with any surgical procedure, the use of general anesthesia also carries risks, including allergic reactions and respiratory problems.
Infection:
Infection can occur at the incision site or around the implant.
Bleeding and bruising:
With the manipulation of tissue during surgery, local blood vessels may be damaged, causing bleeding or bruising.
Hematoma:
Blood collection in the surgical area
Capsular contracture:
Formation of tight scar tissue around the implant. This can cause your implants to become misshapen, displaced, painful, or more visible
Implant rupture or leakage:
Implants are not designed to be life-long. Breast implants can rupture or leak, requiring surgical intervention to replace them.
Changes in nipple or breast sensation:
Some women may experience temporary or permanent changes in nipple or breast sensation following surgery.
Pain and discomfort:
Pain and discomfort are common after breast augmentation surgery, but they are usually temporary and can be managed with medication. Post-cesarean section care
Wrong or faulty position of the implant:
This may require additional surgery or intervention to correct the position of the implant.
Scarring:
The extent and visibility of scarring can vary depending on factors such as incision location and individual healing.
Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL):
This immune system cancer is sporadic, but has happened in patients who have received breast implants that have rough or textured surfaces.
If you have breast augmentation you will need to perform regular examinations of your breasts to assess your health and the condition of your breast implants.
Prepare for breast augmentation
What should I wear to a breast augmentation consultation?
Feel free to arrive at your initial consultation wearing loose and comfortable clothing. Because you will be removing clothing at one point during your consultation, you’ll want to wear something you can easily change out of for the physical examination by Dr.
Additionally, wearing a supportive bra without padding or underwire can be helpful, as it provides a natural shape and allows the surgeon to assess your breasts better.
What happens at a consultation for breast augmentation?
In preparing for breast augmentation, Your surgeon will ask you detailed questions about your medical history, you may be asked to:
- What medications you are taking or adjust your current medications
- Your allergies history
- Your smoking history and stop smoking
- Prior surgeries
- Any previous issues you’ve had with your breasts, including lumps, previous mammograms, and any family history of breast issues
- Get a blood test
- Avoid taking aspirin and certain anti-inflammatory drugs as they can increase bleeding
- Stop taking recreational drugs, such as cocaine
To prepare for your procedure, you’ll need to follow preoperative instructions from your surgeon. You’ll probably be advised not to eat or drink starting at midnight the night before your procedure.
What types of breast implants are available?
There are several types of breast implants commonly used in cosmetic and reconstructive breast surgery. These implants differ in material composition, shape, texture, and size. Here are some of the main types:
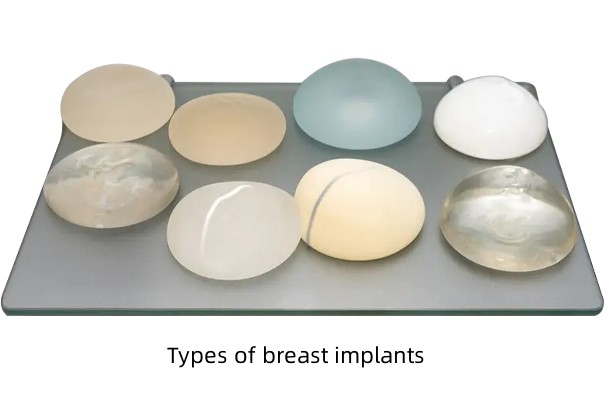
1. Silicone Gel Implants:
These implants are filled with silicone gel. The gel feels a bit more like natural breast tissue. So, They are the most commonly used type of breast implant.
Silicone breast implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women aged 22 or older.
2. Saline Implants:
These implants are filled with sterile salt water. They are often chosen for their adjustability in size and lower cost compared to silicone implants. However, they may not feel as natural as silicone implants.
Saline breast implants provide a uniform shape, firmness, and feel, and are FDA-approved for augmentation in women age 18 or older.
3. Structured Implants:
These implants have an internal structure designed to mimic the feel of natural breast tissue and have a more anatomical shape, resembling a teardrop or a natural breast contour. They may be filled with sterile salt water or silicone gel.
4. Gummy Bear Implants (Form-Stable or Highly Cohesive Silicone Gel Implants):
These implants are filled with a thicker, form-stable silicone gel that maintains its shape even if the implant shell is broken. They are designed to mimic the natural shape of the breast and provide long-lasting results.
Gummy bear implants can result in a more aesthetically pleasing outcome, reduce the risk of silicone leakage or migration in the event of implant rupture, reduce the risk of rippling, and longevity, among other benefits. But gummy bear implants may also have limitations, such as a potentially higher cost, a firmer feel compared to traditional implants, and a longer incision requirement for insertion.
5. Round Implants:
These implants are symmetrical in shape and provide fullness to both the upper and lower poles of the breast. They are often chosen for a more dramatic increase in breast size or cleavage.
Because round implants are the same shape all over, there is less concern about them rotating out of place.
6. Textured Implants:
The outer surface of these implants has a rough texture, which is thought to reduce the risk of capsular contracture by promoting tissue adherence to the implant. However, they are less likely to move around inside of the breast and become repositioned.
7. Smooth Implants:
These implants are the softest feeling. They can move with the breast implant pocket, which may give more natural movement.
Smooth implants come in a variety of shapes and sizes, allowing for customization to achieve the desired outcome based on the patient’s anatomy. Compared to textured implants, smooth implants may be less expensive, have a lower risk of rippling, and be inserted through smaller incisions.
8. Teardrop or Anatomical Implants:
These implants have a tapered shape, resembling the natural slope of the breast. They are often chosen for a more subtle enhancement and to achieve a more natural-looking result.
9. Hybrid Implants:
These implants combine characteristics of both saline and silicone implants, such as having a silicone shell filled with saline solution.
It can be seen that there are several types of breast implants on the market to choose from. Which breast implant to choose, your cosmetic surgeon will help you choose this based on your proportions and goals.
Where the procedure may be done?
- Surgeon’s office-based surgical facility
- Outpatient surgery center
- Hospital outpatient
- Hospital inpatient
Remember that it’s crucial to choose a board-certified plastic surgeon with experience in breast augmentation procedures and ensure that the facility meets appropriate safety standards.
How to do breast augmentation surgery step by step?
While breast augmentation surgery can be performed using different surgical techniques, the steps are essentially the same in each case, and breast implant surgery can be customized to the patient’s unique needs.
A breast augmentation procedure includes the following steps:
Step 1:General Anesthesia
General anesthesia is commonly used in breast augmentation surgery to ensure that the patient is completely unconscious and unable to feel any pain during the procedure.
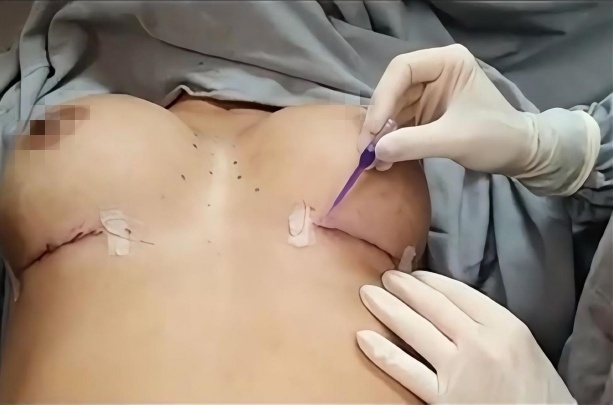
Step 2:The incision
Normally, incisions are made in inconspicuous areas to minimize visible scarring. Common incision locations include:
1. Inframammary Incision(the inframammary fold)
This approach provides good access for placing the breast implant and allows for precise placement.
2. Periareolar Incision (along the areola edge, where the darker skin meets the lighter skin of the breast. )
Generally, this method isn’t suitable for women with small areolas or those who wish to breastfeed in the future, as it can potentially interfere with milk ducts.
3. Axillary incisions (in the armpit)
The advantage of this approach is that there are no visible scars on the breast itself. However, there is a slightly higher risk of breast implant malposition.
4. Transumbilical Incision (TUBA)
Making an incision in the belly button (umbilicus), breast implants are placed into the breast pocket through endoscopic surgery. This method does not leave scars on the breasts, but it is only suitable for certain types of implants and has a higher rate of complications.
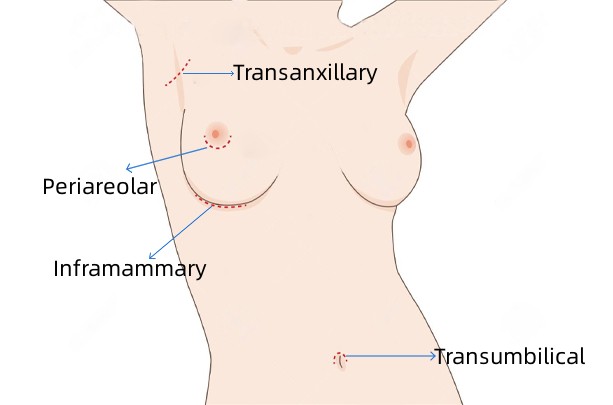
The choice of incision type depends on the patient’s anatomy, the type and size of the implant, the surgeon’s expertise, and the patient’s preferences. Your plastic surgeon will recommend the most appropriate approach based on your circumstances.
Step 3: Create the pocket, insert, and place the breast implant
After the incision is made, a breast implant is inserted into a pocket either:
A. Under the pectoral muscle (a submuscular placement)
B. Directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle (a submammary/sub-glandular placement)
The method for inserting and positioning breast implants depends on the type of implant, the patient’s anatomy, and your surgeon’s recommendations.
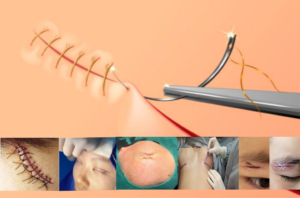
Step 4: Closing the incisions
Incisions are closed with layered sutures in the breast tissue and with sutures, wound skin glue to close the epidermal skin. The incisions are then typically covered with sterile dressings or surgical tape. Traditional vs Cosmetic Sutures
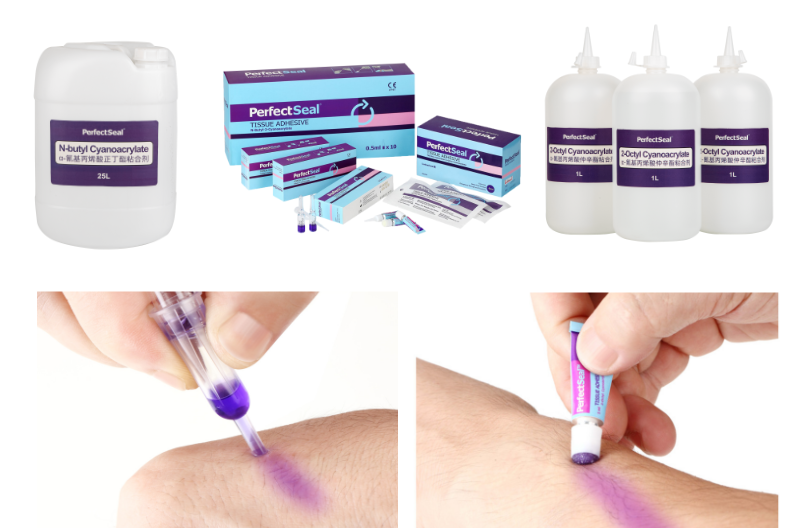
The video of using PerfectSeal wound skin glue to close surgical incisions after breast augmentation surgery.
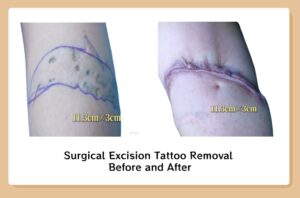
Over time the incision line marks fade. The appearance of a scar depends on several factors, including your genetics, exposure of your body to nicotine, and infection.e
Benefits of using wound skin glue to close breast augmentation surgery incisions
Wound skin adhesive may provide an alternative for wound closure in this setting, with the potential benefit of faster application, decreased operative time, lower risk of infection, faster healing, less scarring, and reduced pain.
Types of wound skin glue
Wound skin glue also known as surgery adhesive, or topical skin glue, is used in medical procedures to close wounds or incisions. Two types of surgery adhesive are commonly used, including n-butyl cyanoacrylate adhesive and 2-octyl cyanoacrylate adhesive.
The difference between n-butyl cyanoacrylate adhesive and 2-octyl cyanoacrylate adhesive.
Step 5: Wearing Surgical Bra
The initial bandages will be replaced in a day or two with a special surgical bra, which should be worn for several weeks. This will help in faster healing and the breast tissue will acquire a new shape.
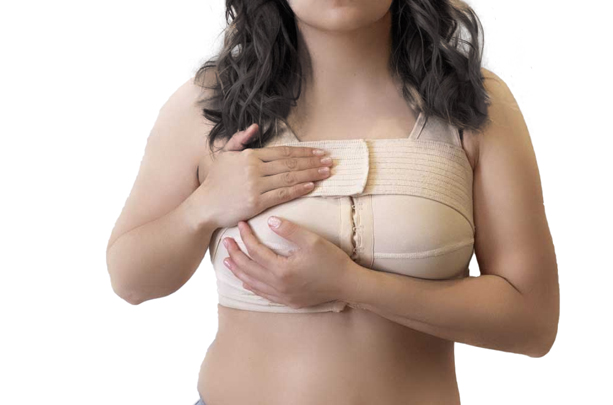
Step 6: See the result
The results of breast augmentation are immediately visible.
Recovery
Immediately after surgery, you will be taken into a recovery area for close monitoring. Your condition is stable enough to go home.
Before leaving, you will receive a discharge report, instructions for post-operative recovery, and a follow-up appointment with your plastic surgeon.
Generally, surgeons recommend wearing a sports bra 24 hours a day for up to 3 months after breast surgery.
Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for at least a month. Resume exercise and normal activity according to your plastic surgeon’s directions.
Result
Beyond the physical changes, breast augmentation surgery can have positive emotional and psychological effects, boosting self-confidence and body image.
FAQ
Does insurance cover breast augmentation?
Insurance usually will not cover breast enlargement surgery. But, if the procedure is deemed medically necessary for reasons such as breast reconstruction after a mastectomy or to correct a congenital deformity, insurance may provide coverage.
What is stem cell breast augmentation?
Stem cell breast augmentation is accomplished with the patient’s body fat, which is natural to the touch and in appearance. Using liposuction techniques, excess fat is harvested from a troublesome area, such as the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, or back. The fat is then purified and injected with micro-cannulas into the breasts for augmentation.
Is breast augmentation safe?
The vast majority of people with breast implants experience no serious complications.
Difference between breast augmentation and breast implants.
Augmentation is the procedure necessary for breast enhancement, while implants are the mechanism used.
When do breast augmentation stitches dissolve?
Depending on your recovery, stitches may be removed after one week, or left to dissolve in the next six to eight weeks. If using tissue adhesive to close the surgery wound, it usually heals more quickly and does not require the removal of stitches.
How long is the recovery for a breast augmentation?
On average, patients take about 6-8 weeks to recover from a breast augmentation procedure fully. Some women feel back to normal after one week of recovery, but everyone has a different experience based on their body, age, health history, and lifestyle.
How long does it last for breast augmentation?
The life span of a breast implant is at least 10 years. For many recipients of breast implants, The service life of these implants might go up to 20 years or more than 20 years.
What is post breast augmentation bra?
A post-breast augmentation bra, also known as a surgical or post-operative bra, is specially constructed with high-quality materials, designed to support your breasts as your tissues recover and provide light compression to promote optimal healing.
REFERENCES
- Adams, William P. Jr. M.D.; Mallucci, Patrick M.D. Breast Augmentation. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 130(4):p 597e-611e, 2012. | DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318262f607. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, David A. M.D.; Spector, Jason A. M.D. Breast Augmentation. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 133(4):p 567e-583e, 2014. | DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000033. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, William P. Jr M.D. The Process of Breast Augmentation: Four Sequential Steps for Optimizing Outcomes for Patients. Plast Reconstr Surg
. 2008;122(6):1892-1900.doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31818d20ec. [PubMed][Google Scholar] - Paul I Heidekrueger 1, Sammy Sinno 2, David A Hidalgo 3, Martín Colombo 4, P Niclas Broer 5. Current Trends in Breast Augmentation: An International Analysis. Aesthet Surg J. 2018;38(2):133-148.doi: 10.1093/asj/sjx104. [PubMed][Google Scholar]
- Ralf Ohlinger 1, Leonie Gieron 1, Rico Rutkowski 2, Thomas Kohlmann 3, Marek Zygmunt 1, Julia Unger 4. The Use of TissuGlu® Surgical Adhesive for Mastectomy With or Without Lymphonodectomy. In Vivo
. 2018;32(3):625-631.doi: 10.21873/invivo.11284. [PubMed][Google Scholar] - Ritu Jain 1, Sarika Wairkar 2. Recent developments and clinical applications of surgical glues: An overview. Int J Biol Macromol
. 2019:137:95-106.doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.208.Epub 2019 Jun 27. [PubMed][Google Scholar]